If you have used GKE then you would most certainly know that it's very restrictive
also for the demonstration purposes you should be using the following to ensure you can stay with us till the end. so let's begin
A bit of advice make sure you are patient enough to try this
Prequisites
use GKE with autopilot or if you have one make sure you have
standard-rwxstorage class fromfilestore.csi.storage.gke.ioRefer: https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/persistent-volumes/filestore-csi-driver
Make sure you have this. for this follow the enable api button on this docs

we are trying to scale the wordpress so that it can handle a lot of users
for ingress will be going to use the
nginx-ingress-controllerI will be using gcloud cli
# some good prequisties before creating anything to define
# 1. Project_id
# 2. Region where you want to deploy
Script creation
first we want to create the variables for us to use them
gcloud config set compute/region asia-south1
export PROJECT_ID=<PROJECT_ID>
# to enable the following GCloud services
gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com sqladmin.googleapis.com
# Resource we are going to create
CLUSTER_NAME=wordpress-k8s
INSTANCE_NAME=mysql-wordpress-instance
SA_NAME=cloudsql-proxy
# creation of gke
gcloud container clusters create-auto $CLUSTER_NAME
gcloud container clusters get-credentials $CLUSTER_NAME
# now you can run this to get the cluster status
kubectl cluster-info
# for creating the Cloud managed GKE service
gcloud sql instances create $INSTANCE_NAME
export INSTANCE_CONNECTION_NAME=$(gcloud sql instances describe $INSTANCE_NAME \
--format='value(connectionName)')
gcloud sql databases create wordpress --instance $INSTANCE_NAME
CLOUD_SQL_PASSWORD=$(openssl rand -base64 18)
gcloud sql users create wordpress --host=% --instance $INSTANCE_NAME --password $CLOUD_SQL_PASSWORD
# creating a IAM service account and adding policy for the upcomming gcloud db proxy
gcloud iam service-accounts create $SA_NAME --display-name $SA_NAME
SA_EMAIL=$(gcloud iam service-accounts list \
--filter=displayName:$SA_NAME \
--format='value(email)')
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--role roles/cloudsql.client \
--member serviceAccount:$SA_EMAIL
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create key.json \
--iam-account $SA_EMAIL
# at this moment we are just need to create 2 secrets for them to be used by the deployment
kubectl create secret generic cloudsql-db-credentials \
--from-literal=username=wordpress \
--from-literal=password=$CLOUD_SQL_PASSWORD
kubectl create secret generic cloudsql-instance-credentials \
--from-file key.json
# save it as wordpress_cloudsql.yaml.template
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: wordpress
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
app: wordpress
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: wp-pv-claim
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
storageClassName: "standard-rwx"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany # so that pods which will get deployed on other nodes, still can mount this PVC
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: wordpress
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: wordpress
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
containers:
- image: wordpress
name: wordpress
env:
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_HOST
value: 127.0.0.1:3306
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cloudsql-db-credentials
key: username
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cloudsql-db-credentials
key: password
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: wordpress
volumeMounts:
- name: wordpress-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/www/html
# Change ${INSTANCE_CONNECTION_NAME} here to include your GCP
# project, the region of your Cloud SQL instance and the name
# of your Cloud SQL instance. The format is
# $PROJECT:$REGION:$INSTANCE
- name: cloudsql-proxy
image: gcr.io/cloudsql-docker/gce-proxy:1.33.2
command: ["/cloud_sql_proxy",
"-instances=${INSTANCE_CONNECTION_NAME}=tcp:3306",
"-credential_file=/secrets/cloudsql/key.json"]
securityContext:
runAsUser: 2 # non-root user
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
volumeMounts:
- name: cloudsql-instance-credentials
mountPath: /secrets/cloudsql
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: wordpress-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: wp-pv-claim
- name: cloudsql-instance-credentials
secret:
secretName: cloudsql-instance-credentials
# it basically replaces any environment variable from current terminal session to the variable placeholder
cat wordpress_cloudsql.yaml.template | envsubst > wordpress_cloudsql.yaml
kubectl apply -f wordpress_cloudsql.yaml
within a few minutes you can see that pods are up and running
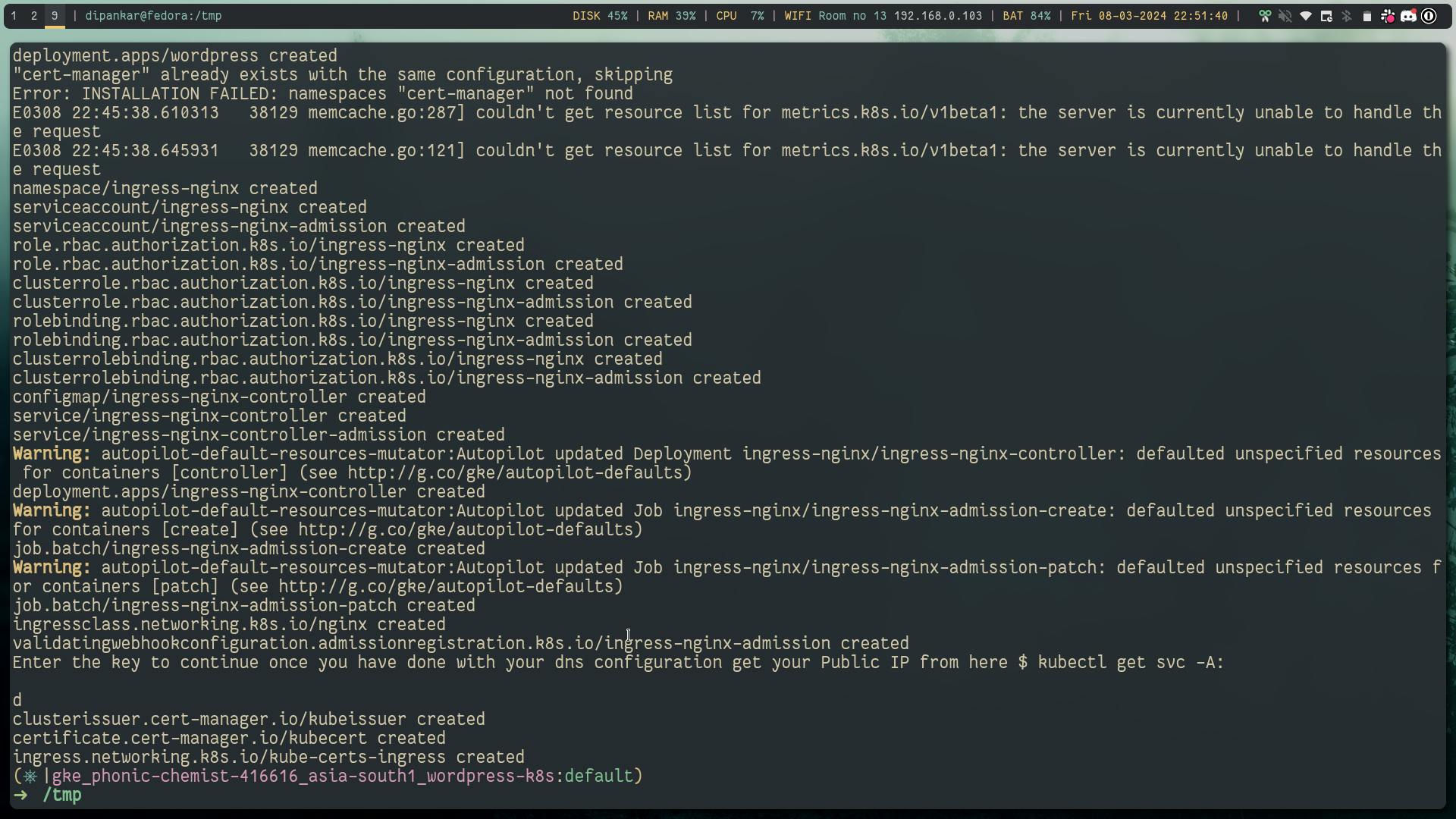
# lets install certmanager and nginx ingress controller
helm repo add cert-manager https://charts.jetstack.io
kubectl create ns cert-manager
helm install my-cert-manager cert-manager/cert-manager --version 1.14.3 --set installCRDs=true --set global.leaderElection.namespace=cert-manager
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.10.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
# create a file name ingress.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: kubeissuer
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: <EMAILADDRESS>
privateKeySecretRef:
name: kubeissuer
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
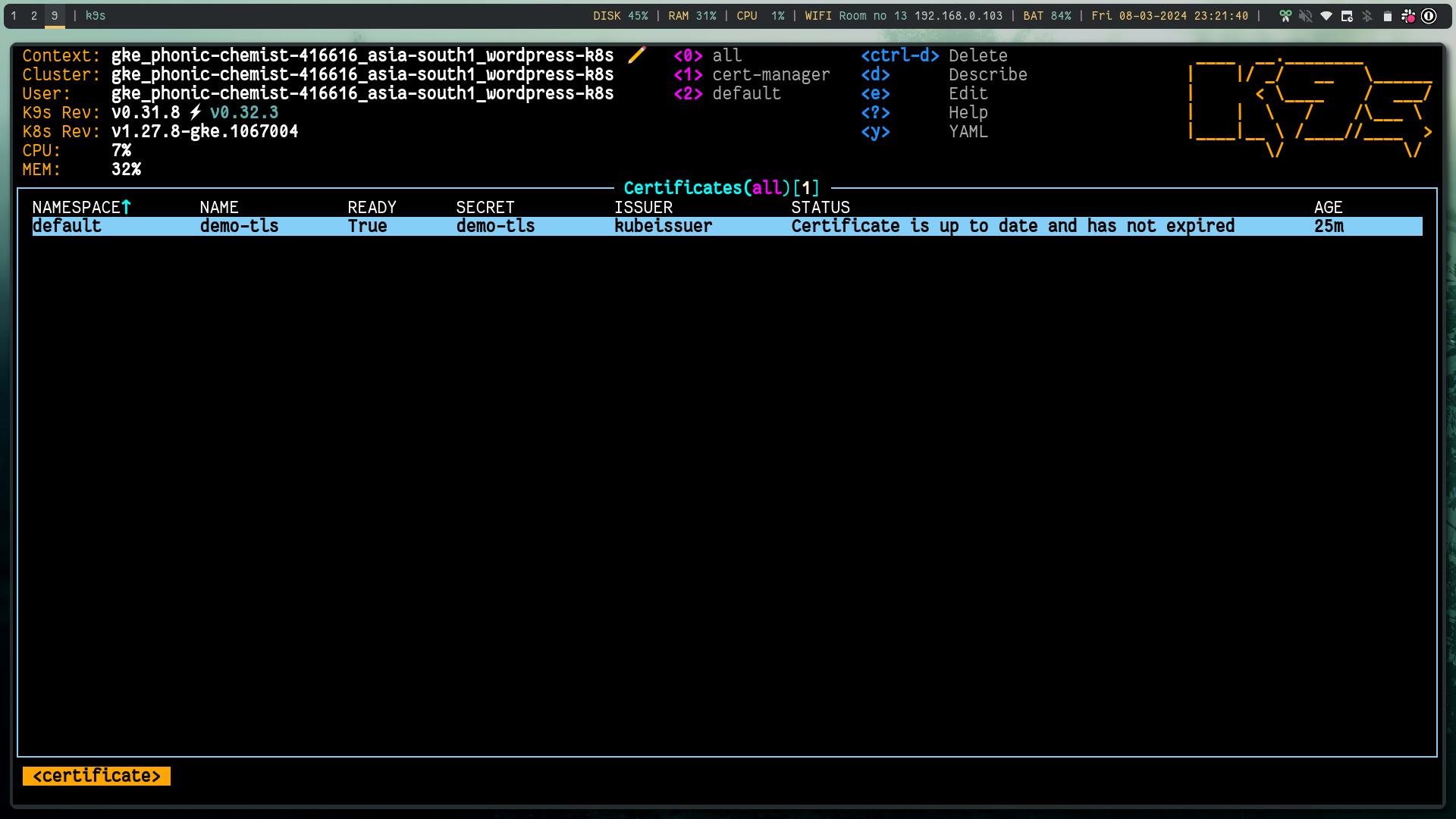
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: kubecert
spec:
secretName: demo-tls
issuerRef:
name: kubeissuer
kind: ClusterIssuer
commonName: <FQDN>
dnsNames:
- <FQDN>
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: kubeissuer
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: kube-certs-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- <FQDN>
secretName: demo-tls
rules:
- host: <FQDN>
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: wordpress
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
kubectl create -f ingress.yaml
Once thats done you can then check your wordpress website
lets create a script so that we can make it reuse it
make sure you have the components installed!!
gcloud components install gke-gcloud-auth-plugin
# or use dnf or apt
sudo dnf install google-cloud-sdk-gke-gcloud-auth-plugin -y
#!/bin/bash
gcloud config set compute/region asia-south1
export PROJECT_ID=""
gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com sqladmin.googleapis.com
CLUSTER_NAME="wordpress-k8s"
INSTANCE_NAME="mysql-wordpress-instance"
SA_NAME="cloudsql-proxy"
DOMAIN=""
EMAIL=""
gcloud container clusters create-auto $CLUSTER_NAME
gcloud container clusters get-credentials $CLUSTER_NAME
kubectl cluster-info
gcloud sql instances create $INSTANCE_NAME
export INSTANCE_CONNECTION_NAME=$(gcloud sql instances describe $INSTANCE_NAME \
--format='value(connectionName)')
gcloud sql databases create wordpress --instance $INSTANCE_NAME
CLOUD_SQL_PASSWORD=$(openssl rand -base64 18)
gcloud sql users create wordpress --host=% --instance $INSTANCE_NAME --password $CLOUD_SQL_PASSWORD
gcloud iam service-accounts create $SA_NAME --display-name $SA_NAME
SA_EMAIL=$(gcloud iam service-accounts list \
--filter=displayName:$SA_NAME \
--format='value(email)')
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--role roles/cloudsql.client \
--member serviceAccount:$SA_EMAIL
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create key.json \
--iam-account $SA_EMAIL
# at this moment we are just need to create 2 secrets for them to be used by the deployment
kubectl create secret generic cloudsql-db-credentials \
--from-literal=username=wordpress \
--from-literal=password=$CLOUD_SQL_PASSWORD
kubectl create secret generic cloudsql-instance-credentials \
--from-file key.json
cat <<EOF > wordpress_cloudsql.yaml.template
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: wordpress
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
app: wordpress
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: wp-pv-claim
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
storageClassName: "standard-rwx"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany # so that pods which will get deployed on other nodes, still can mount this PVC
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: wordpress
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: wordpress
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
containers:
- image: wordpress
name: wordpress
env:
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_HOST
value: 127.0.0.1:3306
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cloudsql-db-credentials
key: username
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cloudsql-db-credentials
key: password
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: wordpress
volumeMounts:
- name: wordpress-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/www/html
# Change ${INSTANCE_CONNECTION_NAME} here to include your GCP
# project, the region of your Cloud SQL instance and the name
# of your Cloud SQL instance. The format is
# $PROJECT:$REGION:$INSTANCE
- name: cloudsql-proxy
image: gcr.io/cloudsql-docker/gce-proxy:1.33.2
command: ["/cloud_sql_proxy",
"-instances=${INSTANCE_CONNECTION_NAME}=tcp:3306",
"-credential_file=/secrets/cloudsql/key.json"]
securityContext:
runAsUser: 2 # non-root user
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
volumeMounts:
- name: cloudsql-instance-credentials
mountPath: /secrets/cloudsql
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: wordpress-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: wp-pv-claim
- name: cloudsql-instance-credentials
secret:
secretName: cloudsql-instance-credentials
EOF
# it basically replaces any environment variable from current terminal session to the variable placeholder
cat wordpress_cloudsql.yaml.template | envsubst > wordpress_cloudsql.yaml
kubectl apply -f wordpress_cloudsql.yaml
# lets install certmanager and nginx ingress controller
helm repo add cert-manager https://charts.jetstack.io
kubectl create ns cert-manager
helm install my-cert-manager cert-manager/cert-manager --version 1.14.3 --set installCRDs=true --set global.leaderElection.namespace=cert-manager
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.10.0/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
read -p "Enter the key to continue once you have done with your dns configuration get your Public IP from here \$ kubectl get svc -A: "
sleep 1m
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: kubeissuer
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: ${EMAIL}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: kubeissuer
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: kubecert
spec:
secretName: demo-tls
issuerRef:
name: kubeissuer
kind: ClusterIssuer
commonName: ${DOMAIN}
dnsNames:
- ${DOMAIN}
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: kubeissuer
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: kube-certs-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- ${DOMAIN}
secretName: demo-tls
rules:
- host: ${DOMAIN}
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: wordpress
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
EOF


References
https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/helm/#4-install-cert-manager
https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/tutorials/http-balancer
Conclusion
Thank you all I hope you dont have to find solutions for all these
Stay tuned for the HTTPS with gateway api
